Comprehensive, Compassionate Care for Every Woman
Personalized Treatment. Proven Results.
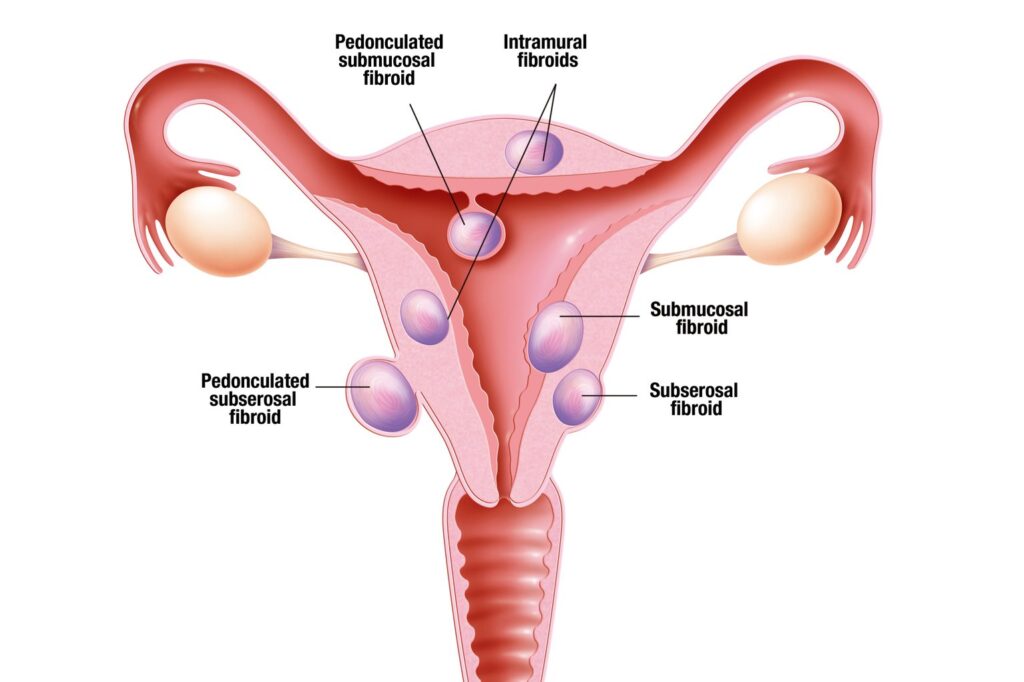
At New York Gynecology Surgery & Endometriosis (NYGSE), our mission is to make advanced treatment options accessible to every woman seeking relief from fibroid-related symptoms. Using the latest robotic and laparoscopic techniques, we’re able to minimize recovery time, preserve fertility when possible, and deliver consistent, long-lasting outcomes. Our patients trust us for precision, compassion, and a level of expertise that few centers can match.