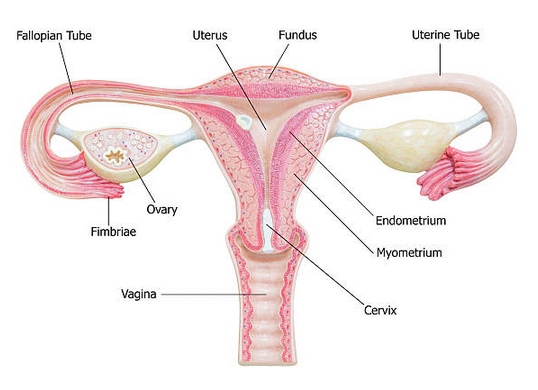
An endometrial biopsy is a medical procedure used to collect a small tissue sample from the lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. This procedure is typically performed by a gynecologist and is used for diagnostic purposes to investigate various uterine conditions and to rule out or diagnose potential issues such as abnormal uterine bleeding, irregular menstrual cycles, postmenopausal bleeding, or to check for the presence of abnormal cells or cancer.
During the procedure, a thin, flexible tube or a suction device is inserted through the cervix into the uterus to obtain a small tissue sample. The collected tissue is then sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination, allowing healthcare providers to assess the condition of the endometrium and determine the presence of any abnormalities or underlying causes for the patient’s symptoms. Endometrial biopsies are generally safe and well-tolerated, and they provide valuable information to guide appropriate medical treatment or further investigations when necessary.
What are the Common Symptoms After Endometrial Biopsy?
Common symptoms that may occur after an endometrial biopsy include mild to moderate pelvic cramping, spotting or light vaginal bleeding, and occasionally, a small amount of vaginal discharge.
These symptoms are generally short-lived and typically resolve within a few days. Some individuals may also experience mild discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvis, akin to menstrual cramps, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
While rare, more severe complications, such as heavy bleeding or infection, may occur, and individuals should promptly consult their healthcare provider if they experience excessive pain, fever, heavy bleeding, or other concerning symptoms after the procedure.
Importance of Endometrial Biopsy
Endometrial biopsy holds significant importance in women’s healthcare for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it serves as a pivotal diagnostic tool for gynecologists and healthcare providers. By obtaining a small tissue sample from the uterine lining, this procedure aids in the accurate diagnosis of various uterine conditions, including abnormal uterine bleeding, irregular menstrual cycles, and postmenopausal bleeding. This diagnostic precision is particularly crucial in identifying underlying causes and tailoring appropriate treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive timely and targeted care.
Endometrial biopsy plays a critical role in the early detection of endometrial cancer and pre-cancerous conditions, such as endometrial hyperplasia. Timely identification of these conditions is paramount for improving treatment outcomes and patient survival rates. Since endometrial cancer often presents with symptoms like abnormal bleeding, an endometrial biopsy can swiftly confirm or rule out cancer, enabling prompt initiation of therapies such as surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy when necessary. Consequently, endometrial biopsy contributes significantly to cancer prevention and the early intervention of potentially life-threatening conditions.
Common Outcome of Endometrial Biopsy
The common outcomes of an endometrial biopsy can include the following:
-
Normal Results: In many cases, the biopsy will reveal that the endometrial tissue is normal. This means there are no signs of cancer, pre-cancerous conditions, or significant abnormalities. Normal results are reassuring and suggest that the patient’s symptoms are likely not related to a uterine issue.
-
Abnormal Findings: Sometimes, an endometrial biopsy may detect abnormalities in the endometrial tissue. These abnormalities can include:
- Endometrial Hyperplasia: This condition involves an overgrowth of the endometrial lining and can range from mild to severe. It is a precancerous condition that may require treatment.
- Endometrial Polyps: Polyps are growths in the lining of the uterus and can cause symptoms like abnormal bleeding. They can often be removed during the biopsy procedure.
- Endometrial Cancer: In some cases, the biopsy may reveal the presence of endometrial cancer. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment, and treatment options may include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
-
Inconclusive Results: Occasionally, an endometrial biopsy may yield inconclusive or insufficient tissue samples for analysis. In such cases, the procedure may need to be repeated to obtain a more definitive diagnosis.
-
Complications: While not common, complications such as bleeding, infection, or injury to nearby structures can occur. These complications are typically managed by the healthcare provider.